The DNP and the RBTDS
The Senegal River Delta Transboundary Biosphere Reserve (RBTDS) was created jointly by Senegal and Mauritania under the aegis of the Program Man and Biosphere of UNESCO.
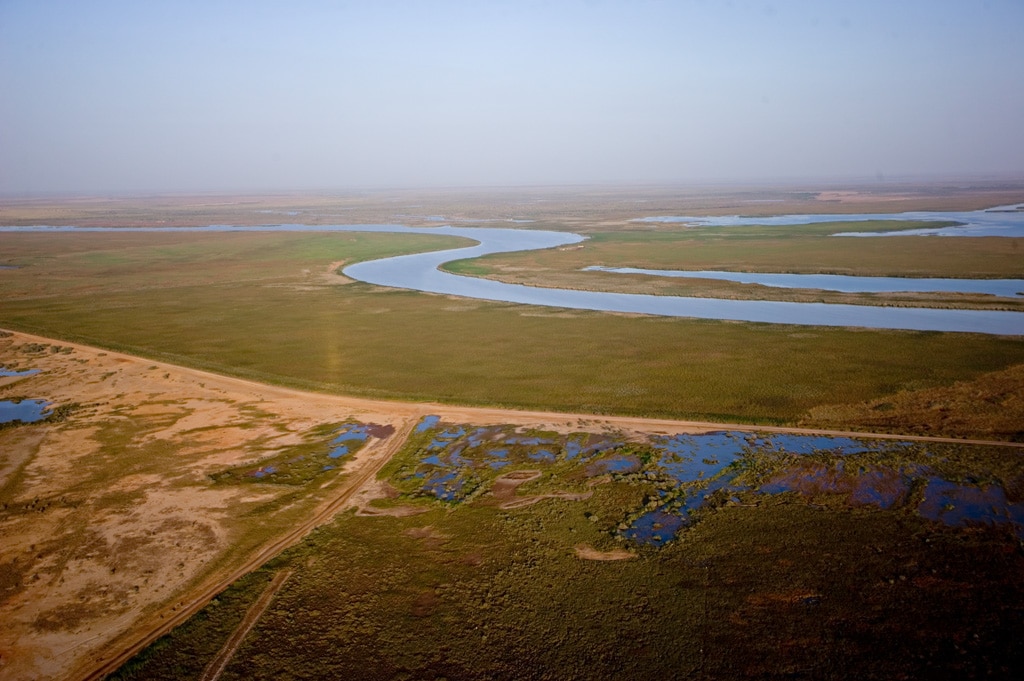

A biosphere reserve classified by UNESCO
Classified by UNESCO on June 27, 2005, the RBTDS covers a total area of 641 ha (186 ha in Mauritania, and 908 ha in Senegal) of which 454 ha are located in the continental zone and 860 ha in the maritime zone.
This reserve includes border sites on both sides of the Senegal River, such as the Diawling National Park, Chat Tboul nature reserve in Mauritania, the Djoud National Bird Park, Barbary language and Guembeul reserve all three of whom are in Senegal.
Cross-border cooperation between Mauritania and Senegal
Its cross-border dimension is necessary by the existence of human settlements and a partly common history on both banks of the Senegal River. Finally, the high level of artificialization which characterizes the delta system following the development of the river requires a coordinated management response, which must be based on increased efforts to better understand the functioning and hydraulicity of this entire vast wetland system.
The approach proposed through the RBTDS must make it possible to bring together national and international capacities and skills serving a true integration of hydrological and conservation management of the delta area, with the aim of preserving both its biological carrying capacity and its socio-economic value for local populations.
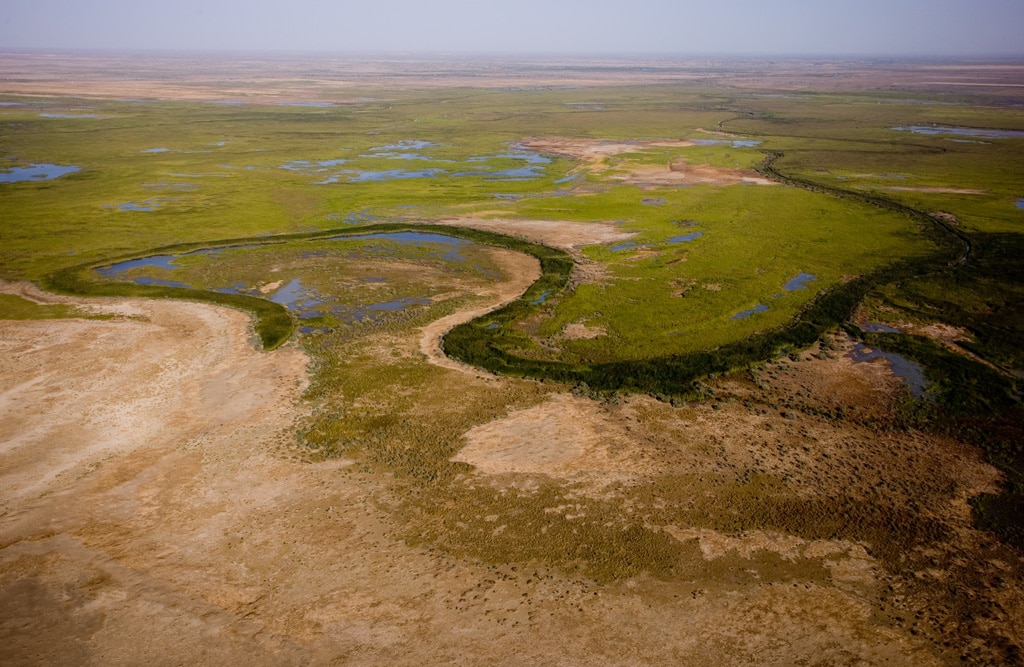

The objectives of the RBTDS
1.
Maintain the current dynamic of ecosystem regeneration
2.
Restore biodiversity while allowing local populations to develop and improve their living conditions by sustainably exploiting natural resources
3.
Extend the achievements of the restoration of natural resources and development of local communities recorded in the PND and the PNOD to other sites
4.
Strengthen the resilience of populations residing in and around the biosphere reserve
The RBTDS right bank has important natural, coastal and marine resources, which provide fundamental ecological services. These resources undoubtedly contribute to economic growth as well as resilience to the effects of climate change, and they provide livelihoods to a population heavily dependent on their productivity.